Misuse of technology is known as cybercrime. Cybercrime is a crime that involves a computer and a network. In cybercrime, the computer and network are targets, weapons and accessories. Cybercrime harms the victim’s network security and financial health. Cybercrime involving the Internet, represents an extension of existing criminal behavior alongside some novel illegal activities.

Types of Cybercrime :
1) Cyber Laundering
Cyber Laundering is the practice of engaging in financial transactions to conceal the identity, source and destination of illegally gained money.

Examples :- Credit/ATM Card fraud, Online Lottery Scam, ATM/Credit card skimming, Credit/ATM Card Cloning.
Punishment :- It is an offense under section – 43, section – 66, and IPC (Indian Panel Code) – 420 penalized under IT Act 2008, up to 2 Lacs, or imprisonment for a term which may extend up to 3 years.
2) Cyber Pornography
Pornography is the initial systematically successful ecommerce product. Deceptive selling techniques and mouse stable gear technologies. Creative activity encourages customers to access their websites. Anybody as well as kids will go online to the web and access websites with sexy content with a click of a mouse.
Punishment :- Publishing, transmitting any material in electronic form which is lascivious or appeals to the prurient interest is an offense under the provisions of section – 67 of IT Act 2008.
3) Identity Theft
Identity theft is the use of the net or other electronic means to stalk or harass a private person, a gaggle of people or a company. It’s going to embrace false accusations, monitoring, creating threats, fraud, harm to knowledge or instrumentality, the solicitation of minors for sex, or gathering info so as to harass. The definition of “harassment” should meet the criterion that an affordable person, in possession of an equivalent info, would regard it as sufficient to cause another affordable person distress.

Punishment :- Identity theft is an offense under the provisions of section – 43, section – 66, section – 67, section – 67A, section – 72 of IT Act 2008 and IPC (Indian Panel Code) 509, 465 and punished with imprisonment for a term which may extend to 5 years, or with fine which may extend to 10 lacs rupees, or with both.
4) Phishing
Phishing is that the reprehensively fallacious method of trying to accumulate sensitive info like usernames, passwords Associate in Nursing credit card details by masquerading as a trustworthy entity in an transmission, communications purporting to be from widespread social internet sites, auction sites, on-line payment processors or IT directors square measure ordinarily wont to lure the unsuspecting public. Phishing is {often} distributed by e-mail or instant electronic messaging, and it often directs users to enter details at a pretend website whose look and feel square measure nearly a dead ringer for the legitimate one.

Punishment :- An offence under the provisions of section – 43, section – 66D of IT Act 2008 and IPC ( Indian Panel Code) 419, 420, 468 and punished with imprisonment for a term which may extend to 3 years, or with fine which may extend to 1 lac rupees, or with both.
5) Software Privacy
Theft of software packages through the illegitimate repetition of real programs or the counterfeiting and distribution of merchandise meant to pass for the initial. Retail revenue losses worldwide are ever increasing thanks to this crime. It can be done in various ways end user copying, hard disk loading, counterfeiting, illegal downloads from the internet.

Punishment :- An offense under the provisions of section – 43, section -65, section -66 of IT Act 2008, and 63 of the copyright Act, and punished with imprisonment for a term which may extend to 5 years, or with fine which may extend to 10 lacs rupees, or with both.
6) Spoofing
There are several styles of spoofing techniques that are utilized by the folks to hack the systems or to induce crucial data by showing it as legitimate method.

Examples :- IP spoofing, Content spoofing, Caller ID spoofing, Email spoofing, SMS spoofing.
7) Salami Attack
In such a crime criminal makes insignificant changes in such a fashion that such changes would go unremarked. Criminal makes such program that deducts touch like Rs.2.50 per month from the account of all the client of the bank and deposit constant in his account. During this case no account holder can approach the bank for such quantities; however, criminals gain vast amounts.

8) Virus
Virus means malicious software that attaches itself to other software. Virus, worms, Trojan horses, time bombs, logic bombs are the malicious software.

Punishment :- An offense under IT Act 2008 section – 43, section -66 and IPC (Indian Panel Code) 426 penalizes upto 1 crore Rs.
9) Cyber Terrorism
Cyber terrorist act is outlined because the aforethought use of tumultuous activities, or the threat there from, against computers and/or networks, with the intention to cause hurt or any social, ideological, religious, political or similar objectives, or to intimidate a person in furtherance of such objectives. Terrorist square measure coated by the traditional laws like IPC and special legislation concerning terrorist act.

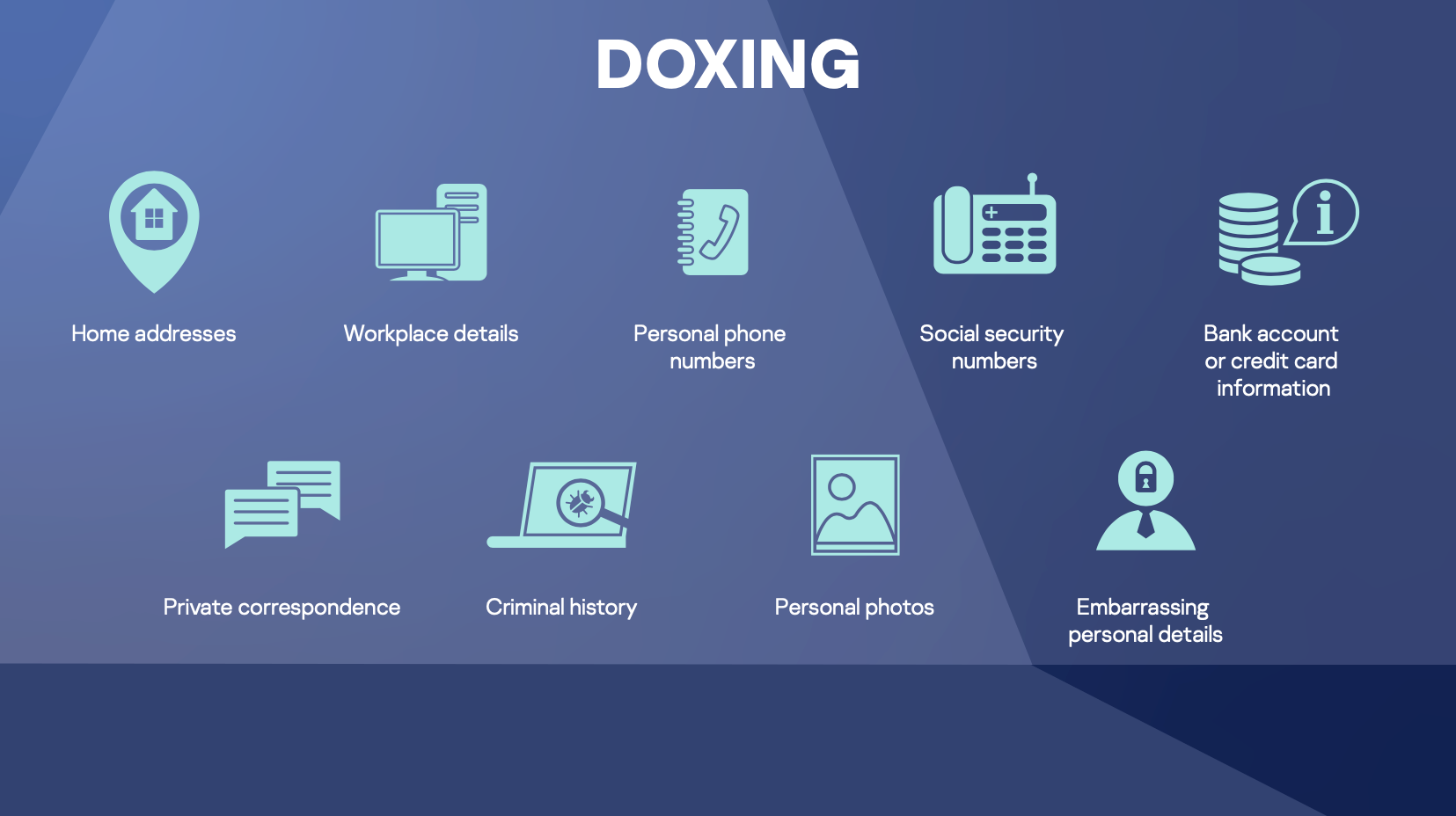
10) Doxing
Doxing, a derivation of the phrase “document tracing”, is the act of scouring the internet for an individual’s personal data, usually for a malicious purpose.
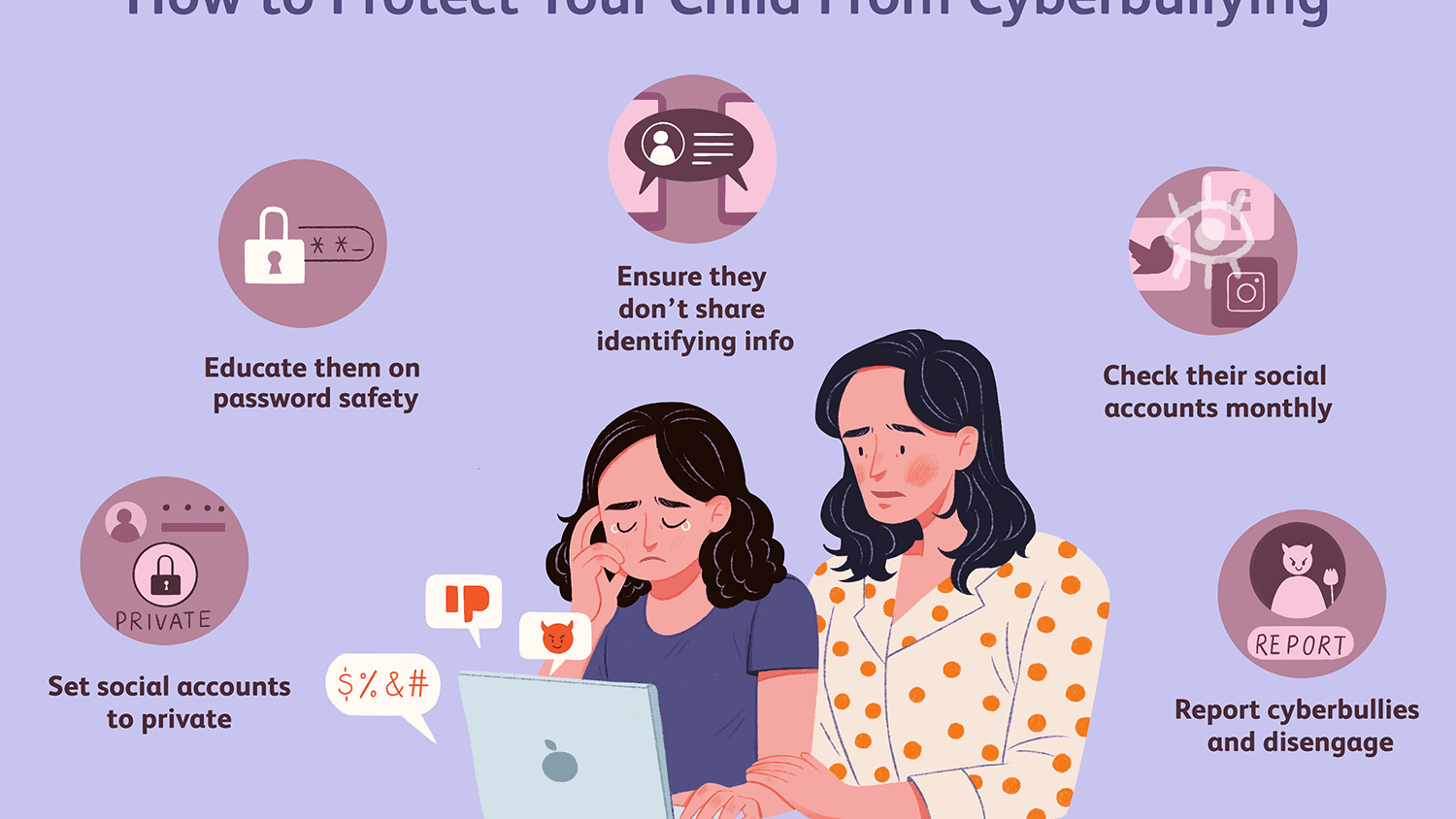
11) Cyber Bulling
Cyberbullying is when a person or a group of people, uses the internet, mobile phones or other digital technologies to threaten, tease or abuse someone. It’s against the law to bully someone in this way, and if someone is being mean or threatening you, something can be done to stop them.